Retrograde Amnesia - Definition, Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
Definition
Retrograde amnesia is one of the two main types of amnesia. It is characterized by an impairment to recall previous events, experiences and even previous familiar information or impairment in the recall of autobiographical memory.
Amnesia is described as a shortfall in memory that may be caused by damage to the brain, psychological trauma or disease. The degree of memory loss can either be partial or whole depending on the severity that caused the condition. Amnesia is divided in two main types describing the form of amnesia and these are:
Retrograde amnesia
It is defined as the incapacity to recollect memories of previous and recent events, experiences and information on the personal life of the affected individual prior to the event or a trauma that resulted to the deficiency in memory. New information or memories on the other hand can still be consolidated while declarative memories are still intact.
Anterograde amnesia
It is the inability to consolidate new information subsequent to an event or trauma that resulted in memory loss or amnesia. Previous events and experience prior to the onset of amnesia on the other hand remains unharmed.
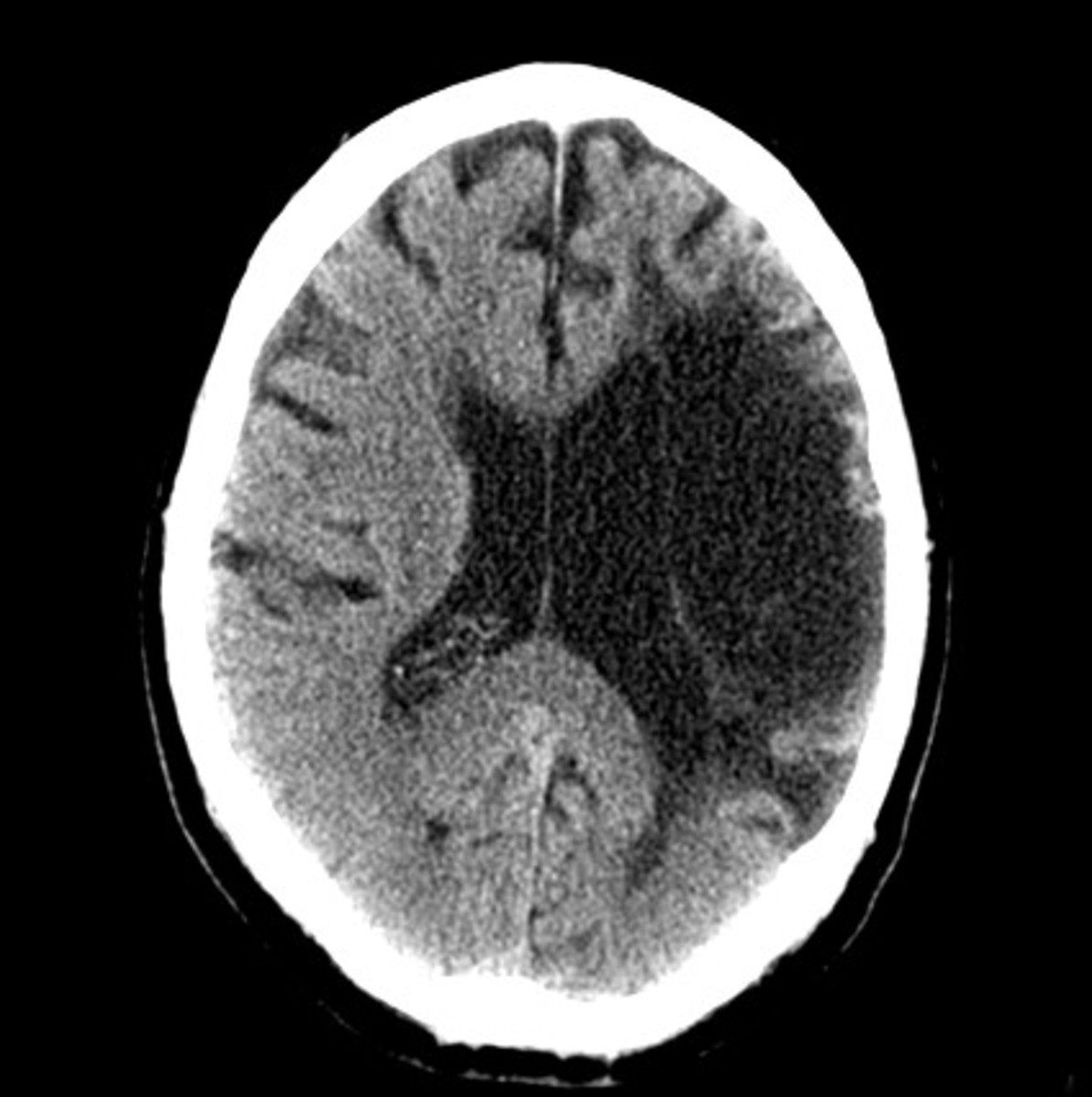
The hippocampus is the part of the brain that is involved or damaged in the onset of amnesia whether retrograde or anterograde type. It is the part of the brain that is responsible for shaping new information as well as organizing and storing it. The hippocampus is part of the limbic system that is vital in creating new memories as well as linking emotions and senses to memory. It functions as a memory indexter that through transmission of memories to the proper region of the cerebral hemisphere for long-term storage and for recovering these memories for later use or when necessary. The hippocampus is also involved in several functions such as in the consolidation of new information, spatial orientation and navigation and also plays an important role for emotional responses.
Symptoms
The onset of retrograde amnesia has various symptoms depending on the extent of brain injury or damage that resulted in deficit in memory.
The common symptoms of retrograde amnesia are as follows:
- Difficulty in recalling non-verbal information
- Long-term loss of memory
- Inability to consolidate language formation
- Inability to coordinate and sort out verbal material
Extreme retrograde amnesia rarely occurs but may cause an individual to suffer from permanent memory loss, even to the extent of failure to recognize their own identity. The memory loss of the patient on the other hand can be selective or categorized. There are also different types of retrograde amnesia which a patient can suffer from such as:
Temporally graded retrograde amnesia is temporary or short term impairment in retrieving memory involving the systemic consolidation. This type of retrograde amnesia is also associated or may have traces of anterograde amnesia.
Pure retrograde amnesia is a pure form of retrograde amnesia and without any trace of anterograde amnesia unlike the temporally graded retrograde amnesia. It is however regarded as a rare form of retrograde amnesia.
Focal retrograde amnesia is a type of retrograde amnesia that also has the traits of anterograde amnesia. No physical abnormalities can be observed in this retrograde amnesia and is more of psychological type instead. This condition is rather characterized with mild anterograde and retrograde amnesia and more of a psychogenic form.
Isolated retrograde amnesia is the extreme form of retrograde amnesia and is linked with visible thalamic lesion. This form of retrograde amnesia is characterized by an extreme inability to recall past events and information.
Retrograde amnesia is the result of damage to the brain particularly in the regions that is linked with the episodic and declarative memory and also includes the autobiographical memory of an individual. The extreme case of retrograde amnesia may have the affected individual completely forget their identity. This form of amnesia however is termed as global amnesia which is known to be the most severe form of amnesia.
Causes
The exact cause of retrograde amnesia has not been clearly established. Both the episodic and declarative memory loss including the autobiographical memory loss is being implicated on damages to certain regions of the brain. The hippocampus is the region of the brain that plays an important role in encoding and storing both the short-term and long-term memory. Damage to this region of the brain is believed to be a factor causing the temporary or permanent loss of memory. The diencephalon is another region of the brain that can be damaged and cause the amnesia. It is part of the brain that transmits sensory information to the cerebral hemisphere and the control functions of the peripheral nervous system. The temporal lobes are part of the cerebral cortex that is responsible for the speech and hearing memory. The function also includes the high level of visual process and memory of an individual that damage to this region of the brain can also result to retrograde amnesia.
Damages in these crucial areas of the brain can be implicated on different factors such as:
Traumatic brain injury is a structural damage to the brain that resulted from an external force such as direct and sharp blow to the head, vehicular accident that can bring a strong impact to the head and brain and a childhood syndrome known as shaken baby syndrome.
Psychologically disturbing events can result to retrograde amnesia without any physical damage to the brain. It is more of an outcome of a traumatic event that drove an individual to consciously or unconsciously forget the traumatic episodes in their life. It could also be an outcome of regular mental and emotional stress episodes.
Nutritional deficiency and chronic alcohol abuse are factors considered to cause damage in the brain. Nutritional deficiency can result to thiamine insufficiency in the brain while chronic alcoholism can lead to erosion in the brain subsequently amnesia.
Infection is also another factor that can cause damage to the brain when the causative agent has reached the brain through the infected bloodstream that circulated in the body.
Treatment
No pharmacological agent can treat retrograde amnesia as there is no specific cause identified. The focus of treatment is more on methods and approach to help reverse retrograde amnesia. Occupational therapy can help a patient in taking new information or can be helped through the use of intact memories as the basis for new information to be gathered and stored. Electronic organizers can also help patient by reminding them of their day-to-day task. Other memory aids can also help in restoring the memory of the patient such as the use of notebooks and wall calendars to help remind the patient of events and other occasions.
Family support can help patients recover what was lost in the memory of an affected individual. Both the family and significant others can help remind patients of eventful memories and help the patient gradually restore their memories.